Linear recirculating ball bearing units
Features
These linear guidance systems are constructed using full complement linear recirculating ball bearing units KUVS..-B and guideways TKVD. They have adjustable clearance and are suitable for long, unlimited stroke lengths.
The linear recirculating ball bearing units can be linked directly to the adjacent construction and thus incorporated into the adjacent construction. This allows very flexible solutions with a low section height.
Since the linear recirculating bearing units are arranged to the sides of the guideway, this gives a large support distance. If the half guideway TKVD14 is used, this gives increased design flexibility.
A guidance system comprises at least two linear recirculating ball bearing units with lubrication connectors supplied fitted, a full guideway or two half guideways and plastic closing plugs.
Full complement
Since they have the maximum possible number of rolling elements, full complement guidance systems have extremely high load carrying capacity and particularly high rigidity.
Linear recirculating ball bearing units
The linear recirculating ball bearing units have saddle plates made from hardened steel and the rolling element raceways are precision ground.
The balls are recirculated in enclosed channels with plastic return elements. A plastic crosspiece running between the end pieces retains the balls in the saddle plate while the linear recirculating ball bearing unit is not yet mounted.
Guideways
The guideways are made from hardened steel and are ground on all faces, the rolling element raceways are precision ground.
The guideways are available with raceways on both sides (TKVD32, TKVD42 and TKVD71) or as a half guideway with raceways on one side only (TKVD14).
Location from above
Guideways TKVD are located from above and have through holes with counterbores for the fixing screws.
Multi-piece guideways
If the required guideway length lmax is greater than the value in the dimension tables, the guideways are supplied as several segments, see link.
Standard accessories
The standard accessories include plastic closing plugs.
Plastic closing plugs
The closing plugs close off the counterbores of the guideway holes flush with the surface of the guideway.
Lubrication connector
Lubrication connectors similar to DIN 3405 for relubrication from the ends are fitted on both end faces.
Load carrying capacity
The rows of balls are in an O arrangement with two point contact on the raceways, ➤ Figure.
The guidance systems can support loads from all directions, except in the direction of motion, and moments about all axes, ➤ Figure.
Their load carrying capacity corresponds approximately to that of the four-row linear recirculating ball bearing and guideway assemblies KUVE, while the rigidity is somewhat lower.
Load carrying capacity and contact angle

Acceleration and velocity
Linear guidance systems with linear recirculating ball bearing units KUVS permit accelerations up to 100 m/s2 and velocities up to 3 m/s, see table.
Operating limits
Designation | Acceleration up to | Velocity up to |
|---|---|---|
m/s2 | m/s | |
KUVS | 100 | 3 |
Interchangeability
Linear recirculating ball bearing units KUVS and guideways TKVD are interchangeable in any combination within one size and accuracy class.
Sealing
End wipers are fitted on both sides to the end pieces of the linear recirculating ball bearing units to retain the lubricant within the system and seal the end faces of the linear recirculating ball bearing unit.
In order to prevent damage to the linear recirculating ball bearing units, the raceways on the guideways must be kept clean.
ACHTUNG
Under extremely heavy contamination load, additional covers must be used.
Lubrication
Linear recirculating ball bearing units KUVS are suitable for oil and grease lubrication. The systems are supplied with an initial greasing.
Lubrication connectors similar to DIN 3405 for relubrication from the ends are fitted on both end faces, ➤ Figure.
Lubrication connector and lubricant reservoir



Operating temperature
As standard, linear recirculating ball bearing units can be used at operating temperatures from –10 °C to +80 °C.
Other temperature ranges are possible by means of special greases.
Corrosion-resistant design
Linear recirculating ball bearing units KUVS are also available in a corrosion-resistant design by means of the special coating Corrotect.
Design and safety guidelines
Preload
In the operation of systems with linear recirculating ball bearing units, setting of the preload must be ensured.
Setting the preload
The preload can be set, for example, by means of pressure screws that can be secured. These are supported in the adjacent construction and act on the back of the linear recirculating ball bearing unit facing the rolling elements. The force ideally acts at the symmetry point of this surface. Application of the preload force is intended to provide clearance-free guidance of the rolling elements in the ball bearing units on the guideways.
Influence of preload on the linear guidance system
The preload of a linear guidance system defines the rigidity of the system.
Increasing the preload increases the rigidity of the guidance system. The preload influences not only the rigidity but also the displacement force of the guidance system. The higher the preload, the larger the displacement force. Furthermore, preload also influences the operating life of the guidance system.
Rigidity
The rigidity is dependent on the preload set.
Location
In order to achieve high rigidity and high load carrying capacity, the guidance elements should be abutted or fixed by dowels against locating faces on both sides.
In order to avoid location defects, the holes in the adjacent construction must be deburred.
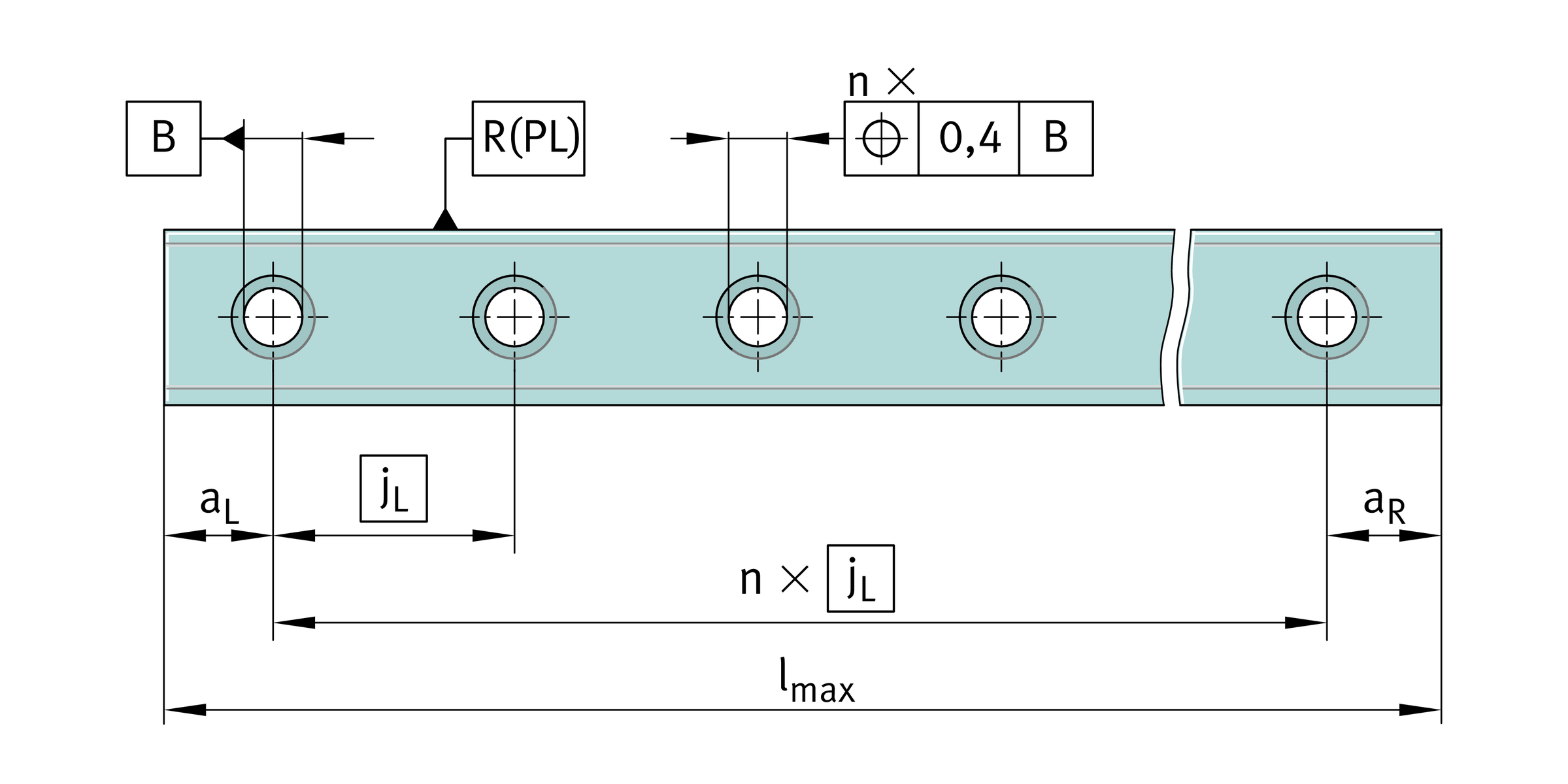
Hole patterns of guideways
Unless specified otherwise, the guideways have a symmetrical hole pattern where aL = aR, ➤ Figure.
An asymmetrical hole pattern may also be available upon request. In this case, aL ≧ aL min and aR ≧ aR min, ➤ Figure.
ACHTUNG
Irrespective of the orientation of the locating face, aL is on the left and aR on the right, ➤ Figure. When ordering, the required orientation of the locating face (top or bottom) must be indicated.
Hole patterns of guideways with one or two rows of holes





Maximum number of pitches between holes
The number of pitches between holes is the rounded down whole number equivalent to: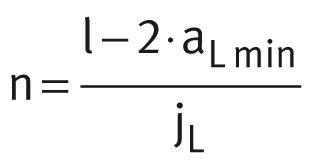 The spacings aL and aR are generally determined as follows:
The spacings aL and aR are generally determined as follows: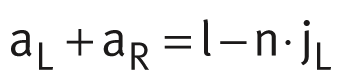 For guideways with a symmetrical hole pattern:
For guideways with a symmetrical hole pattern: 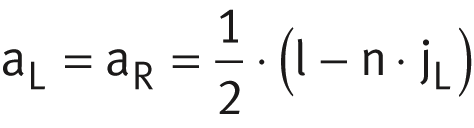 Number of holes:
Number of holes: 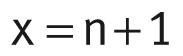
| aL, aR | mm | Spacing between start or end of guideway and nearest hole |
| aL min, aR min | mm | Minimum values for aL, aR |
| l | mm | Guideway length |
| n | – | Maximum possible number of pitches between holes |
| jL | mm | Spacing between holes |
| x | – | Number of holes. |
ACHTUNG
If the minimum values for aL and aR are not observed, the counterbores of the holes may be intersected. Risk of injury.
Multi-piece guideways
If the guideway length required is greater than lmax, see dimension tables, or joined guideways are required, these guideways are made up from segments that together comprise the total required length. The segments are matched to each other and marked, ➤ Figure.
Marking of multi-piece guideways
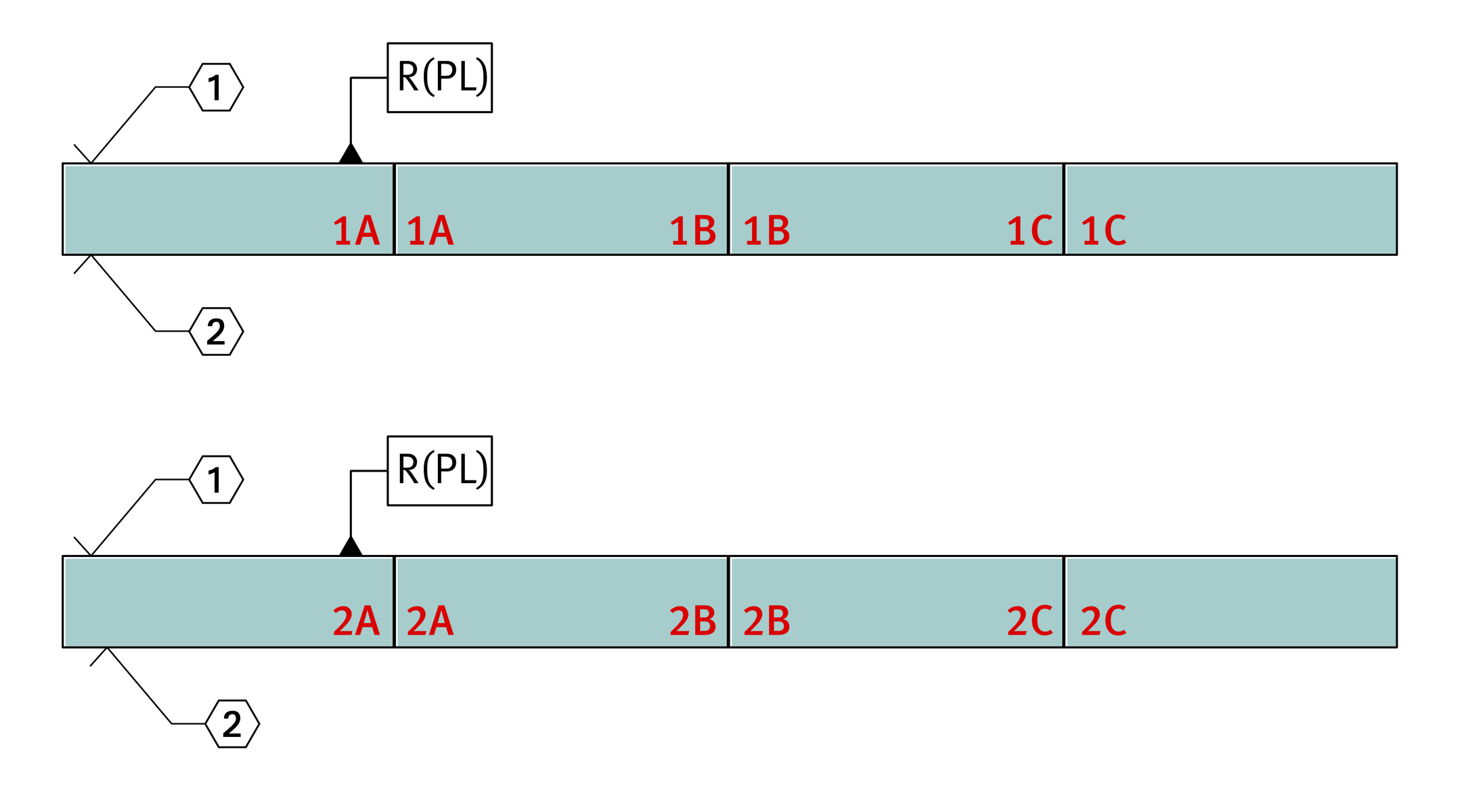


1A, 1A 1B, 1B 1C, 1C
2A, 2A 2B, 2B 2C, 2C
ACHTUNG
In the case of multi-piece guideways, the gap at the end faces between two segments must be < 0,05 mm.
Guideways suitable for joining as required
If partial guideway lengths (l < lmax) are to be combined with each other to form a guideway set as requested by the customer, the following postscript must be added to the order for the relevant guideway segment: “Guideway suitable for joining as required”.
If the guideway segment is an end segment, it is recommended that the guideway end has a chamfer, in order to make it easier to slide the carriages onto the guideway and protect the seals against damage. In this case, the position of the chamfer (left or right) and the position of the locating face (top or bottom) must be taken into consideration when ordering.
The design facilitates easier logistics.
Demands on the adjacent construction
The running accuracy is essentially dependent on the straightness, accuracy and rigidity of the fit and mounting surfaces.
The straightness of the system can be achieved most easily when the guideway is pressed against a locating face.
Geometrical and positional accuracy of the adjacent surfaces
The higher the requirements for accuracy and smooth running of the guidance system, the more attention must be paid to the geometrical and positional accuracy of the mounting surfaces.
ACHTUNG
Observe the tolerances for the mounting surfaces and parallelism of mounted guideways, ➤ Figure and table.
Surfaces should be ground or precision milled with the objective of achieving a mean roughness value Ramax 1,6.
Any deviations from the stated tolerances will impair the overall accuracy, alter the preload and reduce the operating life of the guidance system.
Height difference ΔH
For ΔH, permissible values are in accordance with the following equation:
| ΔH | μm | Maximum permissible deviation from the theoretically precise position, ➤ Figure |
| b | mm | Centre distances between guidance elements. |
Tolerances of mounting surfaces and parallelism of mounted guideways and linear recirculating ball bearing units

Parallelism of mounted guideways
For guideways arranged in parallel, the values for t are in accordance with ➤ Figure and the table. If the maximum values are used, this may increase the displacement resistance.
Values for geometry and position
Guideway** | Parallelism, flatness and perpendicularity |
|---|---|
t | |
μm | |
TKVD14 | 11 |
TKVD32 | 9 |
TKVD42 | 11 |
TKVD71 | 13 |
**In the case of guideway TKVD14, the locating face is the longitudinal face without a raceway.
Locating heights and corner radii
For the design of the locating heights and corner radii, see table and ➤ Figure.
Locating heights, corner radii
Designation | Locating heights | Corner radii | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
h1 | h2 | r1 | r2 | |
mm | mm | mm | mm | |
max. | max. | max. | ||
KUVS10-B | 5 | 5 | 1 | 1 |
KUVS13-B | 5 | 5 | 1 | 1 |
KUVS17-B | 5 | 5 | 1 | 1 |
Locating heights and corner radii for linear recirculating ball bearing unit




Accuracy
Accuracy classes
Guidance systems with linear recirculating ball bearing units are available in the accuracy class G3.
Parallelism of raceways to locating surfaces
The parallelism tolerance of the guideways is dependent on the accuracy class, ➤ Figure.
In coated systems, there may be deviations in tolerances compared with uncoated guidance systems.
Accuracy class and parallelism tolerance of guideways


Tolerances
The tolerances are arithmetic mean values, see table and ➤ Figure. They are relative to the centre point of the screw mounting or locating surfaces of the carriage.
The dimensions H and A1 should always remain within the tolerance irrespective of the position of the carriage on the guideway, see table.
Tolerances for height H and spacing A1
Tolerance | KUVS..-B | |
|---|---|---|
μm | ||
Tolerance for height | H | ±25 |
Difference in height** | ΔH | 10 |
Tolerance for spacing | A1 | ±25 |
Difference in spacing** | ΔA1 | 20 |
**Difference between several bearing units on one guideway, measured at the same point on the guideway.
Datum dimensions for accuracy

Units with coating
In the case of these units, the values for the corresponding accuracy class must be increased by the values for the coating, see table.
Tolerances for coated parts
Tolerance** | Corrotect | |
|---|---|---|
RROC | ||
μm | ||
Tolerance for height | H | +6 |
Difference in height** | ΔH | +3 |
Tolerance for spacing | A1 | +3 |
Difference in spacing** | ΔA1 | +3 |
**Displacement in tolerance zone (guideway and bearing units coated).
**Difference between several bearing units on one guideway, measured at the same point on the guideway.
Positional and length tolerances of guideways
The positional tolerances are not dependent on the guideway length, ➤ Figure, ➤ Figure and tables.
Positional and length tolerances of guideway TKVD14 with one row of holes
Positional and length tolerances of guideways TKVD32, TKVD42 and TKVD71 with two rows of holes

Length tolerances of guideways
Length tolerance | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Dependent on guideway length l | Multi-piece guideways | ||
mm | mm | ||
≦ 1 000 | 1 000 – 3 000 | > 3 000 | |
–1 | –1,5 | ±0,1% | ±3 |
ACHTUNG
If delivery of the guideway as a single piece is not specified in the order, the guideway can optionally be supplied as several segments. Permissible pitch, see table.
Segments for multi-piece guideways
Guideway length** | Maximum permissible number of segments | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
mm | ||||
< | 3 000 | 2 | ||
| 3 000 | – | 4 000 | 3 |
| 4 000 | – | 6 000 | 4 |
> | 6 000 | 4 plus 1 segment each of 1 500 mm | ||
**Minimum length of one segment = 600 mm.

